Book Appointment
Fillup the form to make an appointment with the doctor
Total Knee Replacement Computer Navigation
Component placement in TKA is critical to its ultimate outcome. Traditionally the implants are placed by using a certain set of rules and surgeon eyeballing the procedure. A large number of times patients have a perfect clinical outcome but unfortunately, sometimes the surgeon will be unable to place the components in the desired position and it can have an effect on the final outcome. To avoid this problem “Computer Navigation” principles were developed to help in appropriate placement of the components.
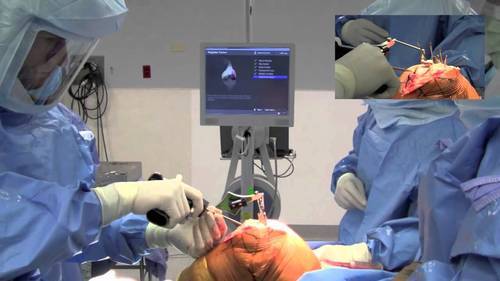
There are broadly 3 different philosophies of navigation. CT scan based, Fluoroscopy based and imageless navigation. The most commonly used technique is the imageless navigation system using infrared sensor marking of the anatomy of the knee and making bony cuts so that the alignment of the component is good. The ideal alignment of the knee is when the components are placed within 3 degrees of the hip, knee ankle axis(Mechanical Axis) but, even in experienced hands, more than 10-20% of the times the components are placed outside this alignment. Using, computer navigation the ability to place the components within this 3 degree is higher and also be able to get a better ligament balance.
It helps in avoiding the outliers (misplacement of the components) and thus we should be able to get an accurate alignment. Better ligament balancing of the knee joint using this technique and gives the surgeon an ability to share the data with his/her patient. It avoids excessive blood loss and possibly reduces the chances of fat embolism
It adds additional costs to the surgery by at least 30,000 rupees. CAS has helped to improve the alignment of the components but has not improved either implant survivorship or has helped in improving the outcomes after a TKA. It adds about 20-30 minutes more to the operating time. There is theoretically a higher chance of fracture with this technique as there are drill holes that are done very close to the components but it is a debatable point at present.
Recently many companies have launched disposable navigation equipment, which can be used to get the same result as the large fixed systems. The advantages of the disposable system are that it can be used in smaller centers and there are no upfront investments for the hospitals as the equipment for CAS is expensive (Around 50 Lakh to 1 crore Indian rupee for the system).
The last decade has seen the introduction of robotics in total knee replacement. Robotic increases the cost of surgery tremendously but has not been of proven benefit in the long term survivorship, outcomes or reduction of complications in knee replacement. At present even in advanced economies robotic is used in less than 5% of cases with the additional financial burden. Robotic knee replacement can be considered niche or cosmetic at present with the available information and computer navigation gives equal or better result in comparison to robotic knee replacement with much less cost to the system.