Book Appointment
Fillup the form to make an appointment with the doctor
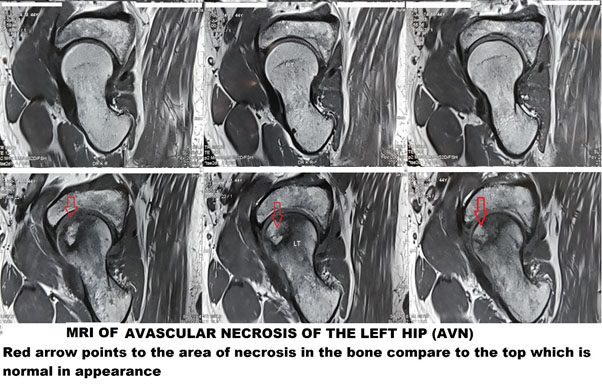
Hip Problems Avascular Necrosis Of The Hip
In AVN, there is a compromise in blood supply to the head of the femur leading to painful progressive hip. This to loss of bone and collapse of the head, eventually leading to arthritis. Majority of the patients are in the 20-40 age group and is commoner in men than women.
There are associations for AVN, but the exact cause cannot be pinned down in all the patients.
1) Idiopathic- this is the largest category where the exact cause is unknown, but patients develop a gradual loss of blood supply
2) Medications- Steroids are potent medication that can reduce blood supply to the head of the femur. It could be a side effect of a necessary treatment where steroids are used. Many times quacks use them for symptomatic relief and can have significant side effects, including AVN.
3) Alcohol – chronic alcohol usage reduces the blood supply and causes AVN
4) Injury – significant trauma, especially to the neck of femur, can cause AVN.
Most people present with dull aching pain in the groin and which can be felt sometimes in the upper thigh. There can be a progressive increase in pain and occasionally early limitation of hip movement. With progressive worsening, there can be a shortening of the affected side and also a pain in the lower back. Examination generally shows limitation in rotation movements of the hip and sometimes flexion.
The primary investigation remains plain x rays. They demonstrate advanced stages quite clearly. In cases of a high index of suspicion and an ordinary-looking x-ray, MRI is the investigation of choice. It demonstrates the stage of the disease and thus guides treatment as well.
There is a lot of controversy regarding the appropriate management of AVN. The early-stage management is the most controversial because the natural history of AVN depends on the amount of necrotic bone in the head, and ultimately has there been a collapse of the head or not.
The medical management consists of Alendronate 10mg/day or 70mg weekly to alter the natural history of AVN. Alendronate belongs to a group of drugs that prevent bone from being resorbed (Osteoclasts) and thus helps in preventing the progression of bone death. Other medications like Statins are found to be useful in some studies in the management of steroid-induced AVN of the hip joint. The statins are suspected to reduce the bone pressure in steroid patients and thus help in preventing AVN.
ECSW (Extra corporal Shock Wave Therapy) and PEMT (Pulsed Electro-Magnetic Therapy) have been tried in the pre-collapse stage of AVN and found to be useful.
ECSW in AVN has, in some studies found to be more useful than core decompression. 4,500-6,000 impulses are delivered in a single sitting to improve the outcome and are cost-effective. It can be performed in an outpatient setting and gives comparable results. The advantage of this technique is it is a one-off event that can be combined with core decompression, and the cost of the procedure is not very expensive.
PEMT- Pulsed electromagnetic therapy has also been in usage for more than two decades now in some European centers. The lack of enthusiasm for universal adoption has been the need for more than 6-8 hour sessions every day for 4-6 months.
Hyperbaric oxygen- This helps prevent the progression of the disease, as shown in a few studies. Lack of availability has made this a difficult option and is mentioned for the sake of completion
Broadly there are three categories of surgical treatment
1) Core decompression
2) Core decompression and augmentation
3) Replacement
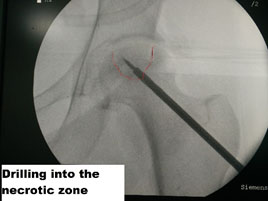
This technique involves the drilling of the femoral head with a drill hole, thereby reducing the intraosseous pressure. This reduction of pressure helps to maintain the remaining blood flow and thus improves the outcome. It is advocated in the pre-collapse phase, and once collapse starts, there is a minimal benefit for core decompression. The success rate of this technique reamed from 30-60%based on the method and the study
This is currently the most confusing field of AVN management. The augmentation might consist of various technique whose cost ranges from a few thousand to more than lakh rupees.
| Surgical technique | Advantages and disadvantages | Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| Fibular grafting | The core decompression is supported with a Fibular strut graft. It has no additional cost, the patient can weight bear early, but donor site pain is common | 55% survivorship at five years and 33% at ten years not needing additional surgical treatment |
| Vascularised Fibular graft | It involves harvesting fibula with its vessels. The fibular and femoral blood vessels are anastomosed by microsurgery, thereby establishing blood supply to the femoral head. Expensive needs micro surgical capability adds more than a lakh to the cost | The odds ratio of conversion to THA is much less with this technique than a non-vascularized fibular graft, but surgical complications are also higher |
| Tantalum rods | The highly porous metal rod which helps to act as a bony scaffold on which bone grows Revision to THA difficult as drilling through tantalum to install femoral stem hard | The expensive technique, no need for bone harvesting and acts like cancellous bone because of its porosity |
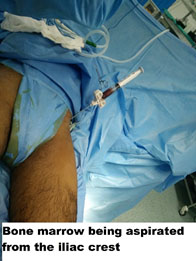
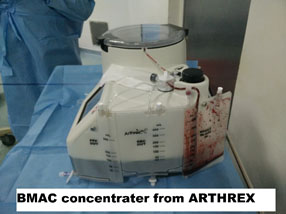
| BMAC with bone debridement | Harvests the patient’s Iliac bone marrow, and the concentrator helps to concentrate the stem cells that can be used after core decompression and debridement of the dead bone with burr
. An additional cost of around 50,000 INR for the surgical procedure |
Mesenchymal stem cells differentiate into osteoblasts (bone cells) after injecting them into the drilled area. Needs the skill to hold it from backflow |
| BMP-7 | This is commercially available bone morphogenic protein which is a growth factor stimulating bone formation Costs up to 1,50,000 INR | Not used independently to quantify the outcome. But, technically makes sense to use this to stimulate bone formation if the patient can afford it |
| Rotational Osteotomy | These are not technically augmentation. But, demanding techniques where the bone is broken and the weight-bearing axis realigned. Difficult later to perform Total hip replacement and currently not preferred | 70% success rate in preventing progression |
24 Year old male presents with early pre-collapse AVN of the hip joint, was treated by core decompression and BMAC (Bone Marrow Aspirate Concentrate).
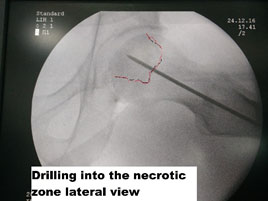
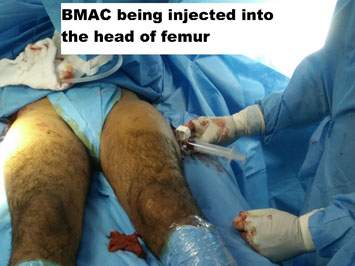
Hip replacement was cited as the operation of the century by the lancet journal and deservedly so. The reasons being the ball and socket joint of the hip can be predictably replaced with advanced metal and plastic components with good functional outcome. AVN is usually the problem of a young age, and though the result of a joint replacement is good when done at a young age is associated with complications. There can be a need for repeat surgery, and joint replacement at a young age has poor outcomes than when done in the elderly. The risk-benefit of appropriate bearing surfaces should also be kept in mind to avoid wear and thus prolong the life of the prosthesis.
A 24-year-old male had taken steroids for cosmetic reasons for three weeks duration only. He has pain in the groin for four years and has not sought treatment. Presently, pain is affecting his quality of life and thus seeking surgical opinion. He was treated with a total hip arthroplasty with ceramic on polyethylene bearing surface.
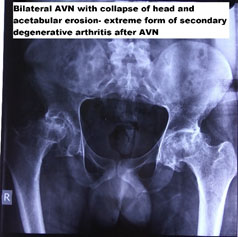
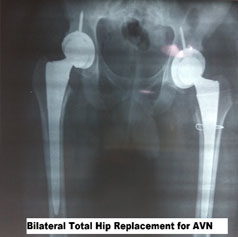
The problem with decision making in surgical management is AVN both for patients and doctors stem from the lack of understanding of the pathology and appropriate intervention at the right time. It takes an understanding of the pathology and proper decision making to influence the ultimate outcome.
In our practice,- we follow the technique of core decompression, debridement of avascular bone with a burr, augmentation with stem cells harvested from the patient himself with precision radiological guidance. If a patient understands the cost-benefit implications of BMP usage, we use it along with allograft substitutes. This “modified cocktail therapy” where a patient undergoes surgical debridement and immediate augmentation along with medication and ESWT help’s in giving the best chance to avoid joint replacement surgery.
The techniques for joint replacement should also be carefully considered. We perform THA in the lateral approach thereby reducing the risk of dislocation along with ceramic bearing to increase the longevity of survivorship of THA.